Nonprofits work hard to address challenges in their communities, but turning good intentions into measurable impact can be quite tricky. That’s where logic models come in.
Logic models can help organizations connect their resources, activities and outcomes, making it easier to plan, track progress and share results with stakeholders.
This guide will explain what a logic model is, why it matters and how nonprofits can create one step by step.
What Is a Logic Model?
A logic model is a visual tool that outlines the relationship between a nonprofit’s resources, activities and goals. Think of it as a roadmap for your organization. It starts with what you invest (time, money, people) and ends with the results you aim to achieve: improved literacy rates, healthier communities or other mission-driven goals, for example. Nonprofits often use logic models to plan projects, measure success or secure funding.
Elements of a Logic Model
Understanding the key parts of a logic model is the first step to creating one. Each element works together to show how your organization operates and what it hopes to accomplish.
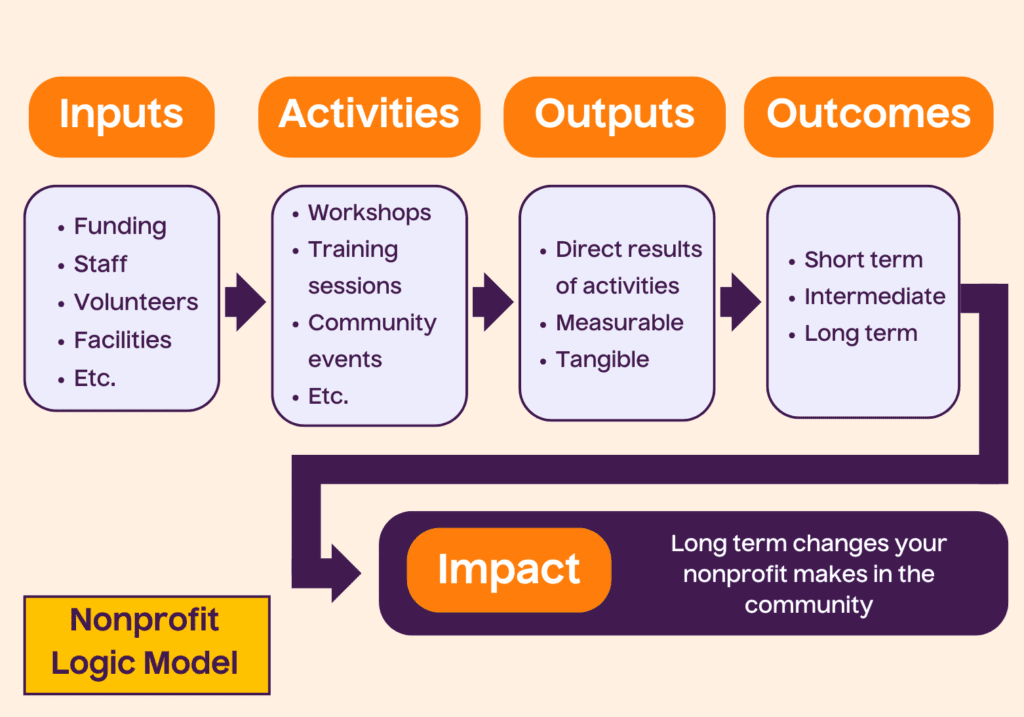
Resources/Inputs
Resources or inputs are what you need to start your work. These include funding, staff, volunteers, facilities and any materials your nonprofit uses to run programs. For example, a literacy nonprofit might list books, tutors and grants as key inputs.
Activities
Activities are what your organization does with its resources. They can include workshops, training sessions or community events. These actions form the foundation of your nonprofit’s programs. If you’re running a food pantry, your activities could include collecting donations, organizing shelves and distributing meals.
Outputs
Outputs are the direct results of your activities. They’re measurable and tangible. For instance, if your nonprofit holds five workshops, the number of attendees at these sessions would be an output.
Outcomes
Outcomes are the changes or benefits that result from your work. These can be short-term, like increased knowledge, or longer-term, like improved financial stability. Outcomes help nonprofits measure their impact over time.
Impact
Impact refers to the broader, long-term changes your nonprofit creates in the community. While outcomes show immediate results, impact speaks to your organization’s ultimate mission. An example would be a health-focused nonprofit aiming to reduce chronic disease rates in its region.
Benefits of a Logic Model for Nonprofits
A well-designed logic model is more than just a planning tool! It’s an asset that strengthens your nonprofit in several ways.
Aligns Resources With Goals
When you understand how resources connect to outcomes, you can make smarter decisions about where to invest your time and money. A logic model helps nonprofits stay focused on activities that lead to meaningful results.
Improves Communication
Clear communication is key for nonprofits working with diverse stakeholders. Nonprofit logic models make it easier to explain your organization’s approach and goals to donors, board members and community partners.
Evaluates Success
A logic model makes progress tracking easier. It provides a structure for assessing whether programs are achieving their intended outcomes and where you might need to adjust.
Supports Grant Applications and Fundraising
Funders often want proof that their money will make an impact. A nonprofit logic model shows exactly how your organization plans to achieve its goals, which can strengthen grant proposals and fundraising campaigns.
Nonprofit Sustainability
Logic models help nonprofits adapt and grow by identifying what works and what doesn’t. They encourage organizations to focus on long-term strategies that, over time, build resilience and sustainability.
How To Create a Nonprofit Logic Model in 8 Steps
Building a logic model might sound intimidating, but breaking it into steps makes the process fairly straightforward. Here’s how you can create a clear and effective model for your nonprofit.
Step 1: Define the Problem or Need
Start by identifying the issue your nonprofit is addressing. Be specific and concise. For example, instead of saying, “We aim to reduce hunger,” you could say, “Our community has a 20% food insecurity rate, particularly among children.” Clearly defining the problem helps you build a focused logic model.
Step 2: Identify Inputs/Resources
List the resources your organization will need to tackle the problem, including funding, staff, volunteers and materials. If your nonprofit provides job training, your inputs could include trainers, computers and partnerships with local businesses.
Step 3: Outline Activities
List the specific actions your nonprofit plans to take to achieve its goals. These could include workshops, community events or educational programs. Each activity should clearly align with the problem you’re working to address and contribute to tangible outcomes.
Step 4: Define Outputs
Outputs are the immediate, measurable results of your activities. For example, if you conduct ten workshops and have 100 participants, those numbers are your outputs. While they don’t show the long-term impact, they’re crucial for tracking progress and keeping stakeholders informed.
Step 5: Determine Expected Outcomes
Outcomes represent the changes your nonprofit aims to achieve through its efforts. Divide these outcomes into short-term, intermediate and long-term categories to highlight how your work progresses over time:
- Short-term: Immediate improvements, like participants gaining new knowledge or skills.
- Intermediate: Changes in behavior or actions that reflect the application of those skills.
- Long-term: Broader, lasting effects that align with your organization’s mission, like improved community well-being or economic growth.
Step 6: Identify Assumptions and External Factors
Every nonprofit operates in a unique environment. Identify the assumptions underlying your logic model, such as the expectation that participants will attend your workshops regularly. Also, consider external factors that could influence your success, like economic conditions or community support.
Step 7: Create a Diagram
Once you’ve outlined all the elements, organize them into a diagram. Most nonprofit logic models follow a left-to-right format, starting with inputs on the left and ending with impact on the right. A visual representation makes it easier to share your model with others.
Step 8: Track Progress and Pivot as Needed
A logic model isn’t static. Use it as a living document that evolves based on your nonprofit’s experiences and data. Review your progress regularly, and adjust activities or resources if outcomes don’t align with your goals.
Nonprofit Logic Model Example
To bring this all together, let’s look at an example. Suppose your nonprofit, Local Harvest Network, is focused on improving access to healthy food in underserved communities.
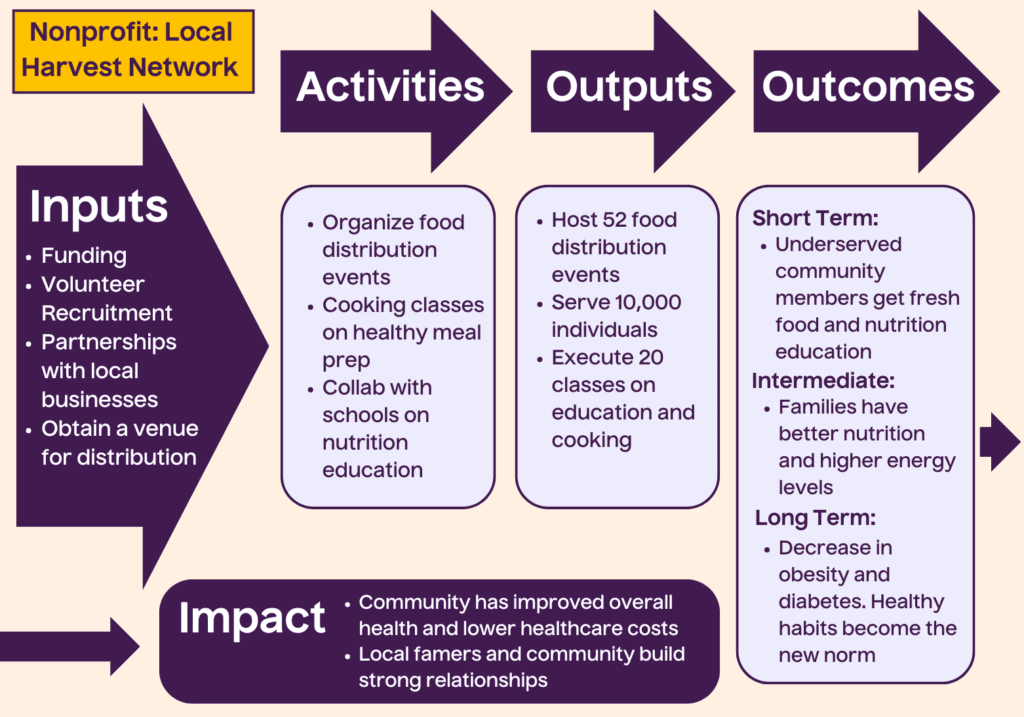
- Inputs: Your organization secures funding, recruits volunteers, partners with local farmers and food distributors, and obtains a community space to serve as a distribution center.
- Activities: You organize weekly food distribution events, provide cooking demonstrations to teach healthy meal preparation and collaborate with schools to offer nutrition education programs.
- Outputs: Over a year, you host 52 food distribution events, serve 10,000 individuals, and conduct 20 educational sessions on nutrition and cooking.
- Outcomes:
- Short-term: Participants gain immediate access to fresh, nutritious food and learn basic cooking techniques.
- Intermediate: Families begin incorporating healthier meals into their diets and report improved energy levels and general well-being.
- Long-term: As healthy eating habits become the norm, the community sees a decrease in diet-related health issues, such as obesity and diabetes.
- Impact: Over time, the region experiences improved overall health, reduced healthcare costs and stronger connections between local farmers and residents.
This example shows how logic models link resources and activities to meaningful results. It can help your nonprofit explain how your work creates tangible benefits, making it easier to demonstrate value and inspire support.
From Planning to Progress: Making Your Logic Model Work
Logic models are a great way to build clarity, track success and communicate impact. By following this guide, your organization can create a logic model that boosts operations, engages stakeholders and drives meaningful change.
To learn more about nonprofit strategy and operations, explore some related blogs on WildApricot:
These tools can complement your logic mode and help your organization achieve its mission!